接續上次【Python】Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹) 資料結構實作(1) 接續來講"Delete"的功能,還沒有看過的可以趕緊補上。
其他資料結構通道:
1. 【Python】Stack(堆疊) 資料結構實作
2. 【Python】Single Linked List(單向鏈結串列) 資料結構實作
3. 【Python】Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹) 資料結構實作(1)
目錄
前言
在 Binary Search Tree 當中,實作刪除節點可以分為以下三個狀況,但在介紹這三個狀況前有些前置作業。
延續上次程式碼【Python】Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹) 資料結構實作(1),我們在 node 新增一個指標 self.parent = None ,讓每個node都可以指向自己的parent,如果沒有parent,代表該node為root node。
class Node:
def __init__(self, value=None):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None #smaller
self.right_child = None #greater
self.parent = None # pointer to parent node in tree在_insert() function 中新增 cur_node.left_child.parent = cur_node 及 cur_node.right_child.parent = cur_node ,讓每字插入node 時每個node都有自己的parent
def _insert(self, value, cur_node):
if value < cur_node.value:
if cur_node.left_child == None:
cur_node.left_child = Node(value)
cur_node.left_child.parent = cur_node #set parent
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value:
if cur_node.right_child == None:
cur_node.right_child = Node(value)
cur_node.right_child.parent = cur_node #set parent
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.right_child)
# value == cur_node.value
else:
print("This value has existed建立好parent的架構之後來談談刪除節點的三個狀況:
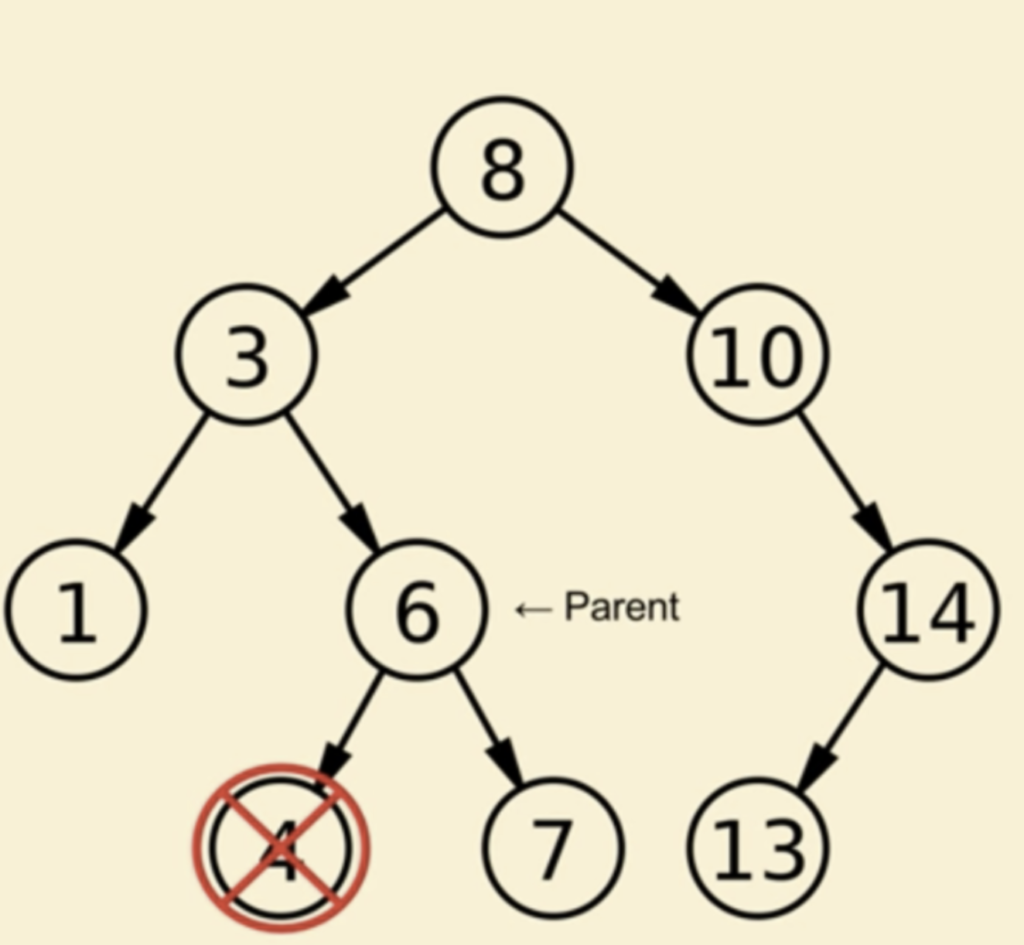
狀況一:刪除節點沒有子節點
在刪除節點沒有子節點的情況下, 只要將該節點指向None解決
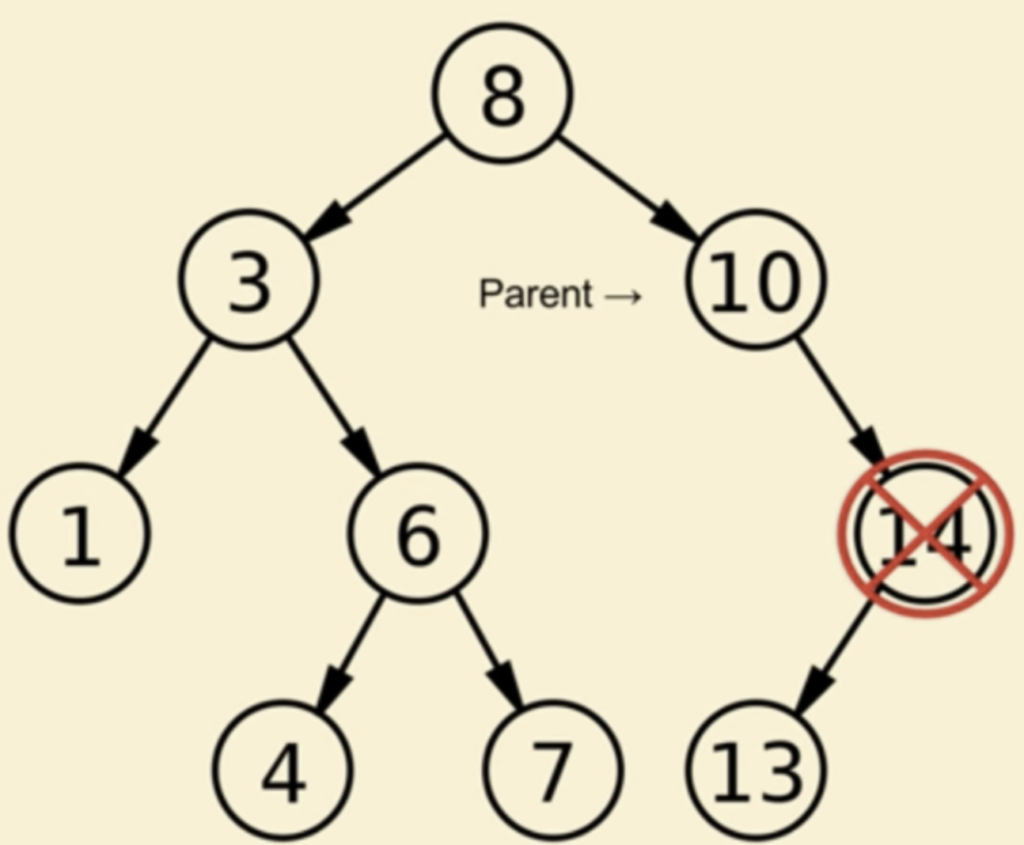
狀況二:刪除節點有「1」子節點
在刪除節點有「1」子節點的情況下,如圖可以發現,將14刪除的話,13的parent會從14變成10,也就是說,刪除14後,10的 right child 會指向13 (記得right node 永遠比 parent大)
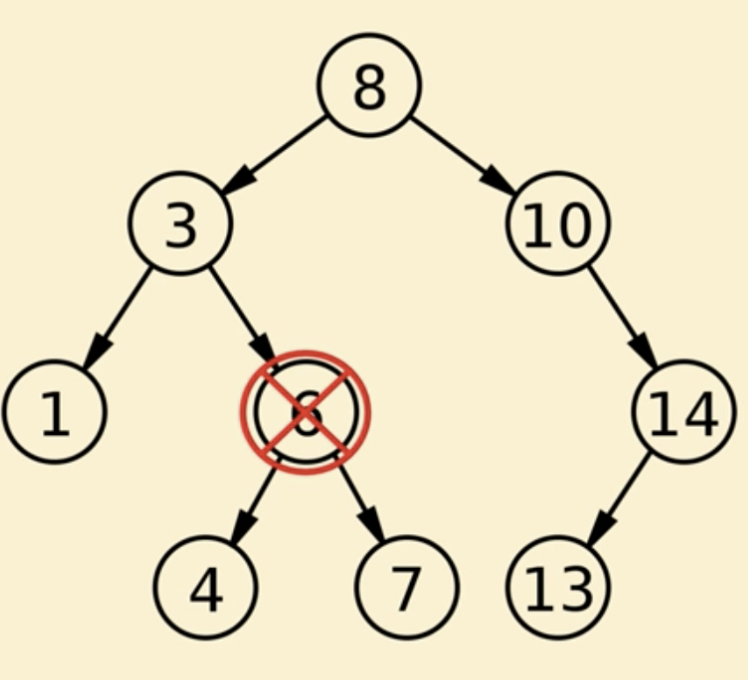
狀況三:刪除節點有「2」子節點
這裡比較複雜,我們要先定一個successor node 也就是要刪除的node的right child,要刪除的node的value等於 successor node 的value,接著就會遞迴呼叫delete function直到successor的 left child指向None。
完整程式碼
class Node:
def __init__(self, value=None):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None #smaller
self.right_child = None #greater
self.parent = None # pointer to parent node in tree
class Binary_search_tree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, value):
#判斷tree是否為空
if self.root == None:
self.root = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, self.root)
def _insert(self, value, cur_node):
if value < cur_node.value:
if cur_node.left_child == None:
cur_node.left_child = Node(value)
cur_node.left_child.parent = cur_node #set parent
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value:
if cur_node.right_child == None:
cur_node.right_child = Node(value)
cur_node.right_child.parent = cur_node #set parent
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.right_child)
# value == cur_node.value
else:
print("This value has existed")
def print_tree(self):
if self.root!=None:
self._print_tree(self.root)
def _print_tree(self,cur_node):
if cur_node!=None:
self._print_tree(cur_node.left_child)
print(str(cur_node.value))
self._print_tree(cur_node.right_child)
def height(self):
if self.root != None:
return self._height(self.root,0)
else:
return
# 我們要在每一次遞迴呼叫時傳入cur_height,如果沒有像parameter
# 樣傳入或儲存成global variable會造成 無法儲存cur_height
def _height(self, cur_node, cur_height):
if cur_node == None:
return cur_height #0
# 找一個最高的子樹
left_height = self._height(cur_node.left_child,cur_height+1)
right_height = self._height(cur_node.right_child,cur_height+1)
return max(left_height, right_height)
# returns the node with specified input value
def find(self, value):
if self.root != None:
return self._find(value, self.root)
else:
return None
def _find(self, value, cur_node):
if value == cur_node.value:
return cur_node
elif value < cur_node.value and cur_node.left_child != None:
return self._find(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value and cur_node.right_child != None:
return self._find(value, cur_node.right_child)
def delete_value(self, value):
return self.delete_node(self.find(value))
def delete_node(self, node):
#returns the node with min value in tree rooted at input Node
#we will pass the single node to treat as the root of a binary search fill_tree
def min_value_node(n):
current = n
# traverse down to the left of the tree until it finds the smallest element returning this value
while current.left_child != None:
current = current.left_child
return current
#returns the number of children for the specified node
# return the number of the children and attach the input node either 0,1 or two
def num_children(n):
num_children = 0
if n.left_child != None:
num_children += 1
if n.right_child != None:
num_children += 1
return num_children
#create variable to hold both the parent of the node to delete as well as
#the number of children get the parent of the node to be deleted
node_parent = node.parent
#get the number of children of the node to be deleted
node_children = num_children(node)
#break operation into different cases based on the
#structure of the tree & node to be delete
#CASE 1 (node has no children)
if node_children == 0:
#remove reference to the node from the node_parent
if node_parent.left_child == node:
node_parent.left_child = None
else:
node_parent.right_child = None
#CASE 2 (node has a single child)
if node_children == 1:
# get the single child node
if node.left_child != None:
child = node.left_child
else:
child = node.right_child
#replace the node to be deleted with its child
if node_parent.left_child == node:
node_parent.left_child = child
else:
node_parent.right_child = child
#correct the parent pointer in node
child.parent = node_parent
#CASE 3 (node has two children)
if node_children == 2:
# get the inorder successor of the deleted node
successor = min_value_node(node.right_child)
#copy the inorder successor's value to the node formerly
#holding the value we wished th delete
node.value = successor.min_value_node
#delete the inorder successor now that it's value was
#copied into the other node
self.delete_node(successor)
def search(self, value):
if self.root != None:
return self._search(value, self.root)
else:
return False
def _search(self, value, cur_node):
if value == cur_node.value:
return True
elif value < cur_node.value and cur_node.left_child != None:
return self._search(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value and cur_node.right_child != None:
return self._search(value, cur_node.right_child)
else:
return False
def fill_tree(tree, num_elems=10, max_int=50):
from random import randint
for _ in range(num_elems): #10個 value
cur_elem = randint(0, max_int) #隨機0~50(不含50)的值
tree.insert(cur_elem)
return tree
#============================================================
#建立1~9的樹
tree = Binary_search_tree()
for num in range(10):
tree.insert(num)
#delete node 5
tree.delete_value(5)
#印出樹
tree.print_tree()結語
Binary Search Tree 的實作到這邊差不多一個段落
邊筆記邊學習
把一個紀錄視為一個結果
累積起來就有舉足輕重的地位
Practice makes perfect.
你可能會喜歡: 【2020】我的Python學習心路歷程 【Django】用Plotly在django中顯示圖表 【Python】畫三角形、菱形、直角三角形 【Python】Stack(堆疊) 資料結構實作 【Python】Single Linked List(單向鏈結串列) 資料結構實作 【Python】Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹) 資料結構實作(1)
推薦入門書籍
精通 Python:運用簡單的套件進行現代運算(第二版)

之前開始入坑python時就是用這本打底的(有換封面過)
這本書除了前幾張介紹基本的語法之外
後續幾張開始介紹與python相關的延伸性的功能
非常適合程式設計初學者以及剛要開始學習這個語言的讀者
羅列以下幾點關於本書大綱供大家參考
- 學習簡單的資料類型、基本數學運算與文字操作
- 以Python的內建資料結構處理資料
- 探索Python程式碼結構,包括函式的使用
- 使用模組與套件編寫大型Python程式
- 深入討論物件、類別與其他物件導向功能
- 檢視一般檔案、關聯式資料庫與NoSQL的儲存機制
- 使用Python建構web用戶端、伺服器、API與服務
- 管理系統工作,例如程式、程序與執行緒
- 瞭解並行處理與網路程式設計的基礎
流暢的 Python:清晰、簡潔、有效的程式設計

適合已經有Python程式語言基礎的人
這本書更詳細的介紹有關python的用法
讓我們寫的程式可以更加"Pythonic"
建議可以與英文版同時閱讀
以後在查閱stackoverflow文獻的時候能不因語言而產生隔閡
- Python 資料模型:瞭解特殊方法是讓物件具備一致行為的關鍵
- 資料結構:充分使用內建的型態,並瞭解 Unicode 時代中,文字 vs. bytes 之間的關係
- 函式就是物件:見識 Python 函式是一級物件,並瞭解這個事實如何影響熱門的設計模式
- 物件導向的習慣用法:學習參考、可變性、介面、運算子多載與多重繼承,並建構類別
- 控制流程:藉由 concurrent.futures 與 asyncio 套件,來充分活用情境管理器、產生器、協同程序與並行
- 中繼編程:瞭解特性、屬性描述器、類別修飾器與中繼類別的工作原理
Python 自動化的樂趣:搞定重複瑣碎&單調無聊的工作(第二版)

如果想使用自動化來增強工作流程效率,大推本書
之前這本書只有英文版
在博客來等了1個月還是沒等到
沒想到在2020/08/28 出了中文版
二話不說馬上看看人家都是怎麼用python來完成例行公事的
除了運用Python寫出程式,在幾分鐘內搞定人工手動處理需要花費數小時的工作。
探索Python豐富的模組程式庫來完成某些特定工作
例如從網站上抓取資料、讀取PDF和Word文件,以及自動化執行滑鼠點按和鍵盤輸入的工作。
‧在一個或多個檔案中搜尋文字
‧建立、更新、搬移和重新命名檔案和資料夾
‧搜尋網頁和下載網路上的圖文內容
‧處理PDF檔的分割與合併,加入浮水印和加上密碼等作業
‧傳送Email和簡訊
‧填寫線上表單
- 【SSH】製作SSH key教學
 製作SSH key 1. 打開終端機(Bash/Terminal) 2. 輸入指令 3. 將指定的 SSH 私 … 閱讀全文
製作SSH key 1. 打開終端機(Bash/Terminal) 2. 輸入指令 3. 將指定的 SSH 私 … 閱讀全文 - 【快速架站】什麼是Hexo? 5分鐘快速架站教學
 What is Hexo? Hexo 是一個快速、簡單且強大的網誌框架。Hexo 使用 Markdown(或其 … 閱讀全文
What is Hexo? Hexo 是一個快速、簡單且強大的網誌框架。Hexo 使用 Markdown(或其 … 閱讀全文 - 【Python】Quick Sort 快速排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門目錄 基本概念實際應用線上學習平台推薦udemy推薦入門書籍精通 Python:運用簡單的套件進行現代運算(第 … 閱讀全文
- 【Python】Insertion Sort 插入排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門目錄 基本概念實際應用線上學習平台推薦udemy推薦入門書籍精通 Python:運用簡單的套件進行現代運算(第 … 閱讀全文
- 【Python】Selection Sort 選擇排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門目錄 基本概念實際應用線上學習平台推薦udemy推薦入門書籍精通 Python:運用簡單的套件進行現代運算(第 … 閱讀全文







程式碼第116行的地方
“num +=1″似乎是筆誤了,應該是要寫成”num_children += 1”
========================
| def num_children(n):
| num_children = 0
| if n.left_child != None:
| num +=1
| if n.right_child != None:
| num_children += 1
| return num_children
========================
感謝指正~,已將文章內容更新👍