目錄
前言
上次寫完 【Python】Stack(堆疊) 資料結構實作 得到了不錯的迴響
這是要來寫寫有關 Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹)
希望大家不要聽到有關「Tree」的資料結構就望而生畏
且聽我在此娓娓道來
本篇文章會帶到以下幾點有關Binary Search Tree該知道的事:
- BST 的 基本概念
- BST 的 Big-O
- Python 實作 BST (加入 node & 印出 tree
你可能會喜歡:【2020】我的Python學習心路歷程
二元樹基本概念
二元樹就是由多個node組成
而BST就是以 node-based 為基礎的資料結構,當中要注意到BST有以下幾點特性:
- node左子樹只會包含比本身還要小得值
- node的右子樹只會包含比自己大的node
- 每個左右子樹都要是二元搜尋樹
- 不可以有值重複的 node
BST Big-O
| Average | Worst Case | |
| Space 空間 | O(n) | O(n) |
| Access 存取 | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Search 搜尋 | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Insertion 加入資料 | O(log n) | O(n) |
| Deletion 刪除資料 | O(log n) | O(n) |
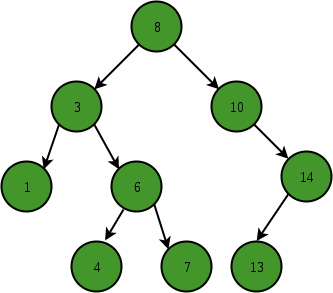
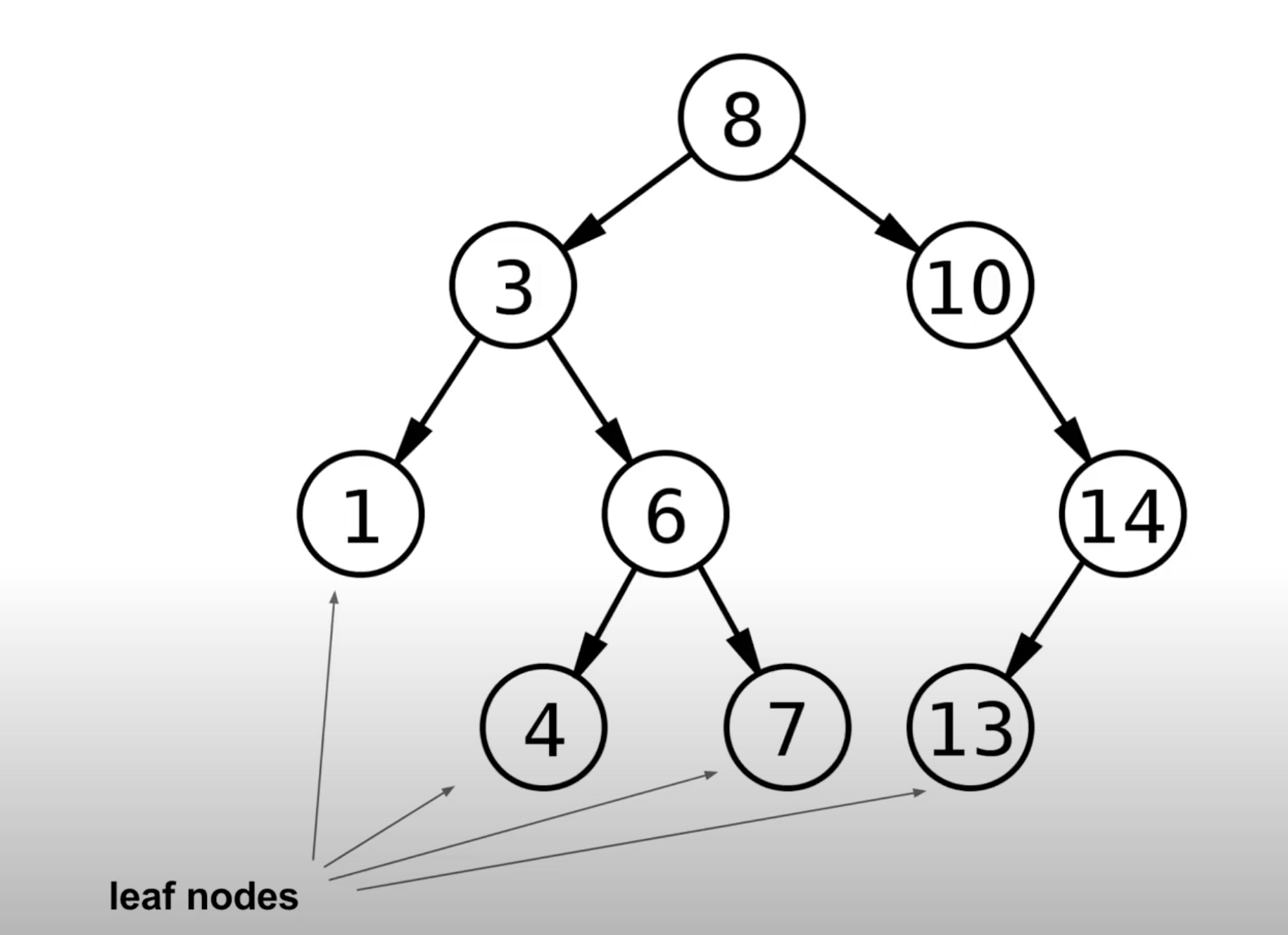
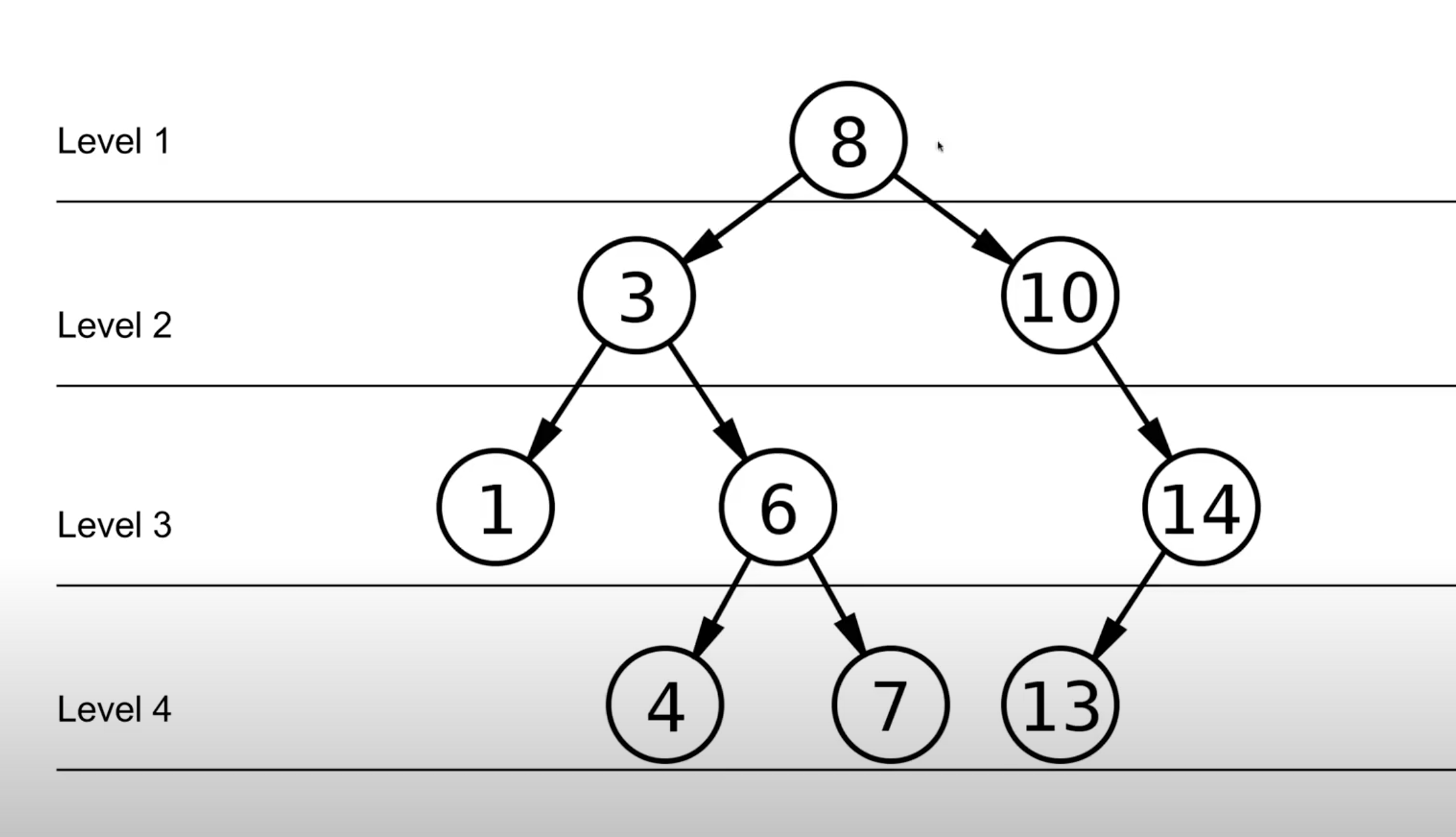
ex: Level 4 的Binary tree 最多可以有 2^4 - 1 = 15 個 node
以上的二元搜尋樹提供了node之間的順序,因此可以快速完成搜索,最小,最大等操作。如果沒有排序,我們就必需比較所有的鍵(key)來搜尋給定的鍵
Full Binary Tree
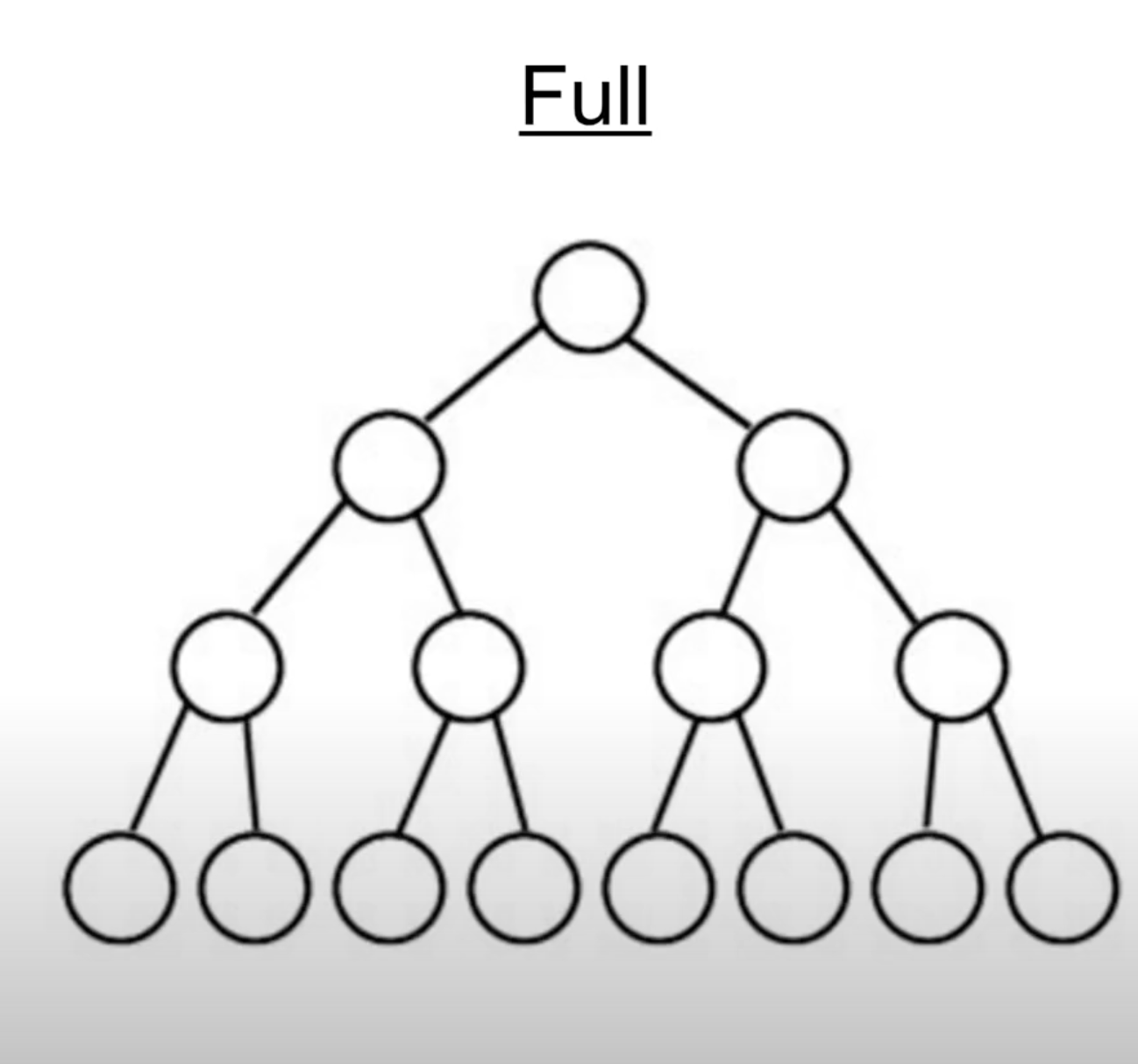
- 所有node都有兩個subtree 子樹 (也就是兩個child pointer);
- 所有leaf node具有相同的level(或相同的height)
- 計算結點數公式為:2^n - 1
ex: Level 4 的 Full Binary tree 一定有 2^4 - 1 = 15 個 node
Complete Binary Tree
一棵樹的node按照Full Binary Tree的次序排列(由上至下,由左至右),則稱此樹為Complete Binary Tree
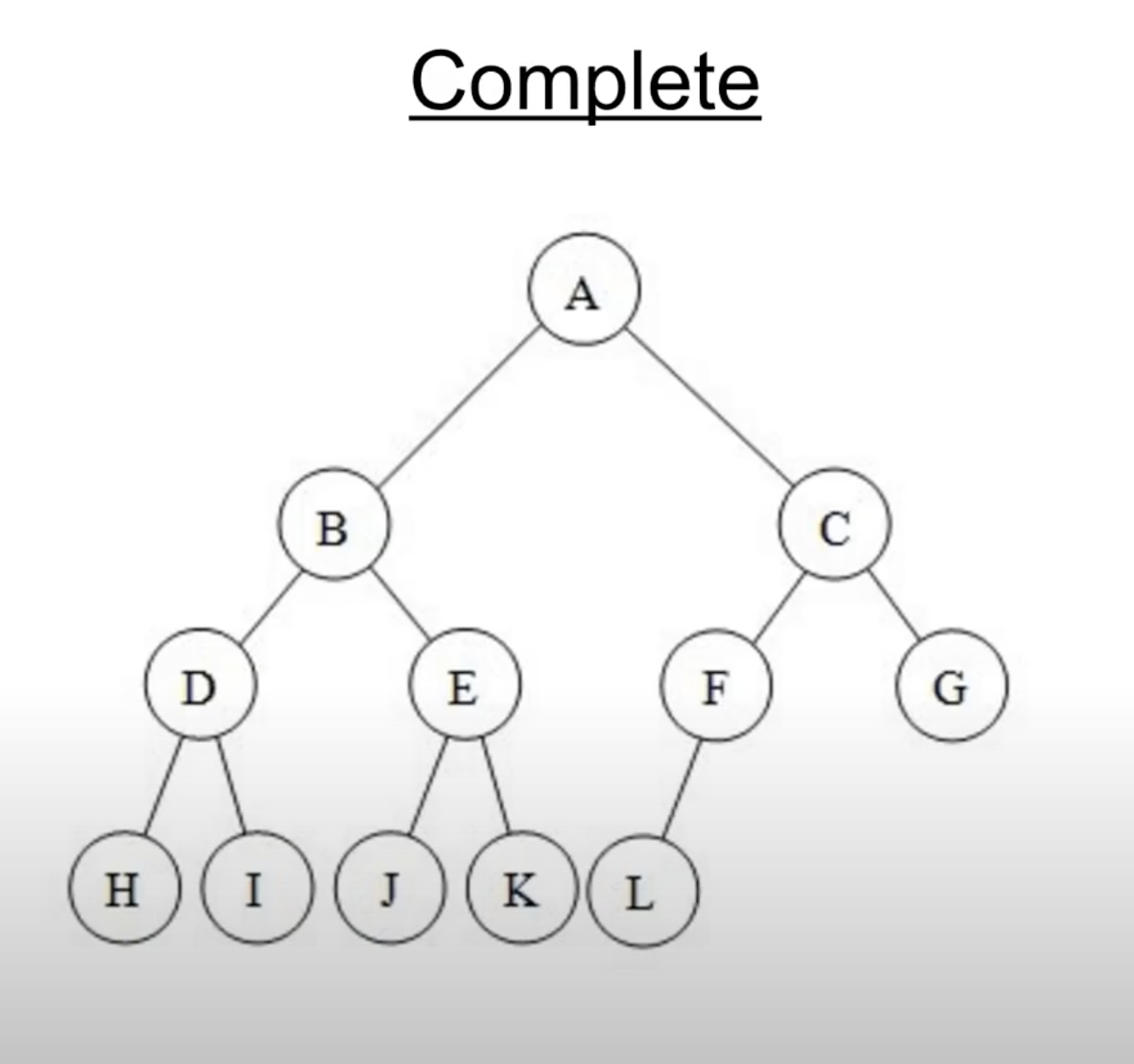
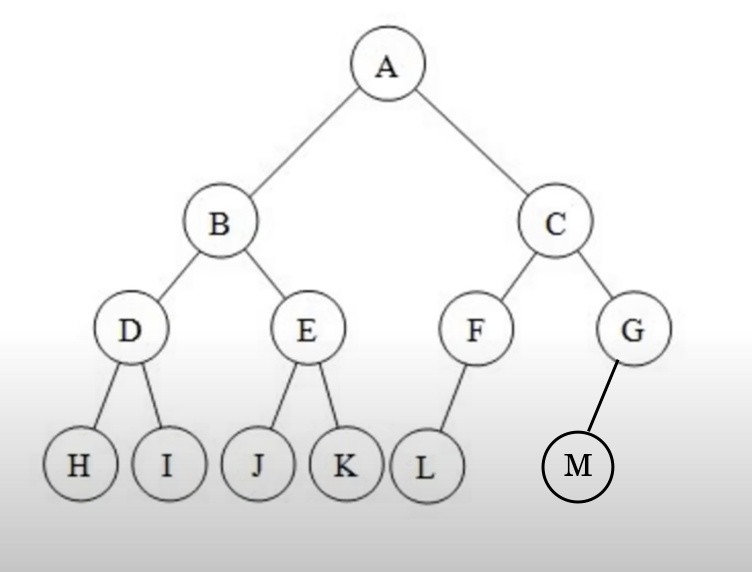
圖6 Node(M)應該要移到 Node(F)的右子樹,因此下圖並沒有滿足Complete Binary Tree的特性
搜尋二元樹
數一定是從root開始找起,不論是刪除,新增等等
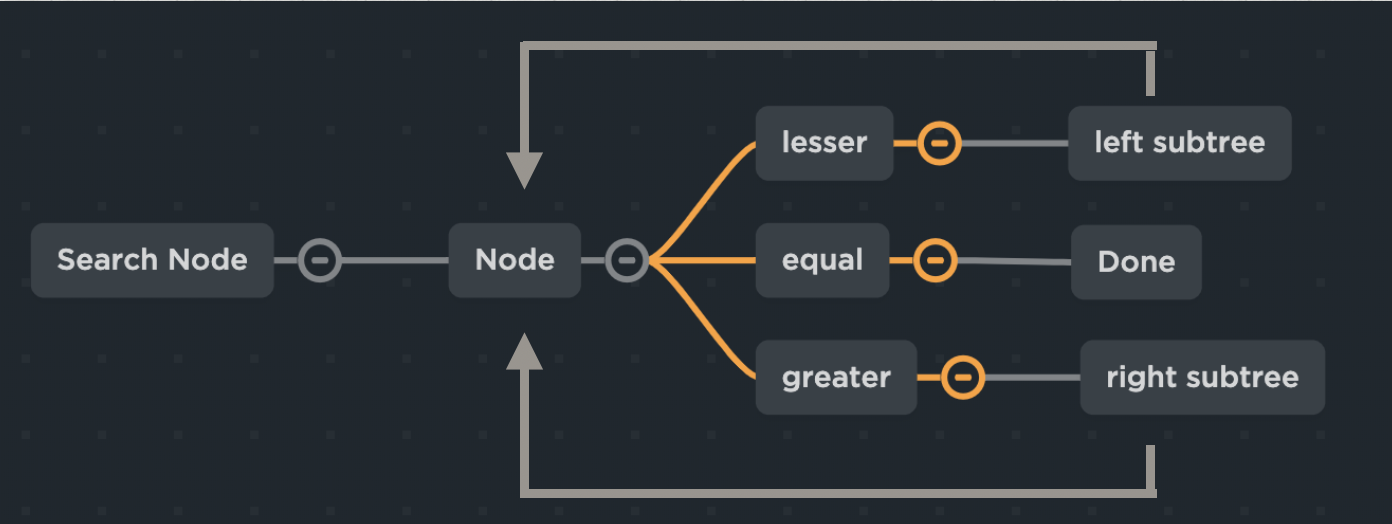
我們將從一個'n'個節點的搜尋Space開始,當我們丟棄(discard)一個子樹時,我們將丟棄'n / 2'個節點,因此我們的搜索Space將減少為'n / 2'個,然後在下一個步驟我們將搜索空間減少到'n / 4',然後繼續像這樣減少直到找到元素(element) 或直到我們的搜尋減少到一個節點(node)為止
新增node
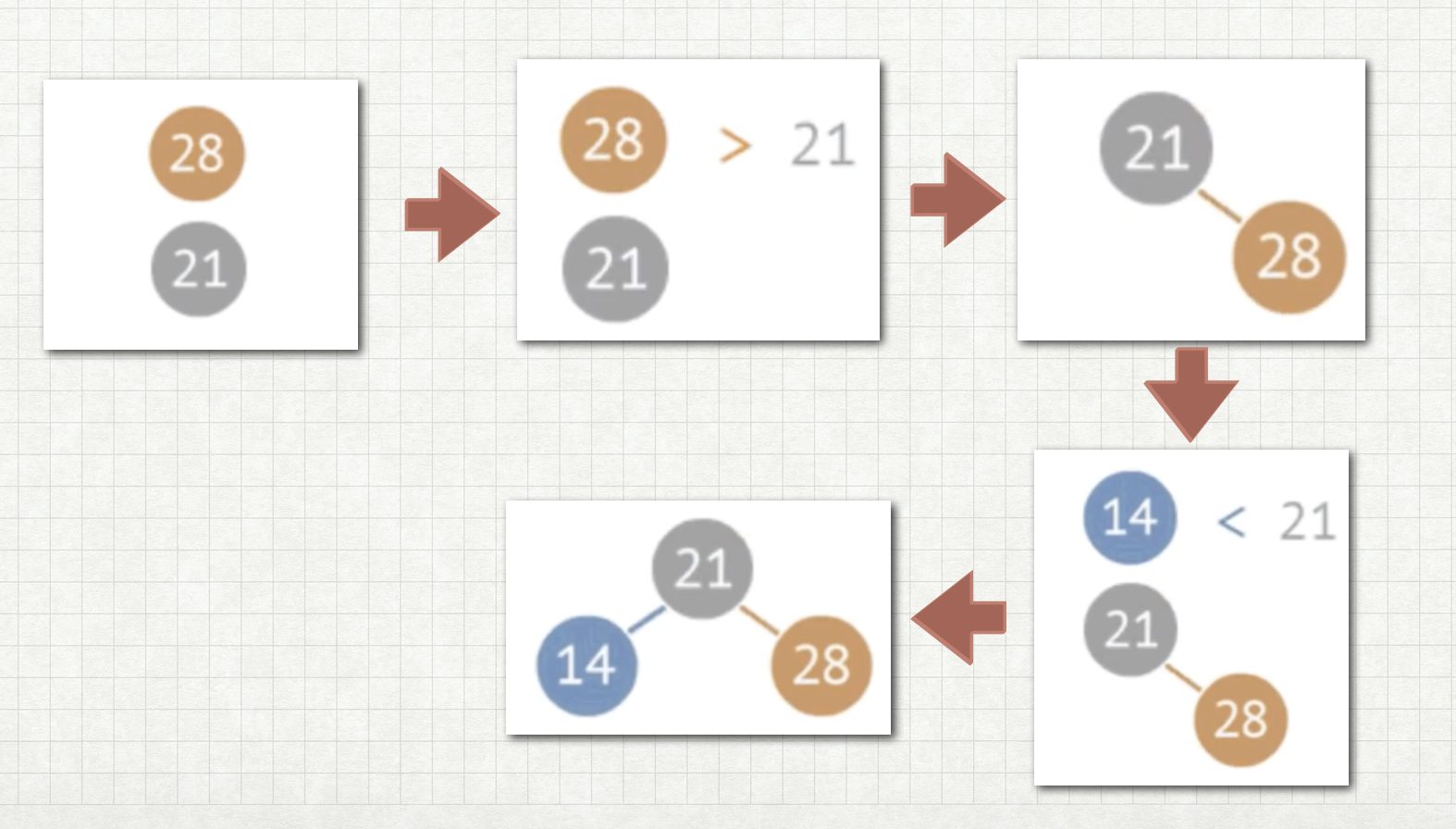
由圖8可知 Node 會先比較 目前的node 如Node(21)
當Node(28) 大於 Node(21) 且 Node(21) 沒有右子樹時 Node(21) 的 右子樹 就會指向 Node(28) 以此類推
你可能會喜歡:【Python】Stack(堆疊) 資料結構實作
Python 實作 BST 二元搜尋樹
首先我們要先建立2個class來讓二搜尋樹動起來
我們要先建立一個 Class Node
將 instructor初始化
一個 node 可以儲存 value ,還有指向 left_child 和 right_child 初始化都指向 None (因為都還沒有資料)
class Node:
def __init__(self, value=None):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None #smaller
self.right_child = None #greater接著要來正式建立 二搜樹的Class了
二搜樹的Class 就好像是 Node 的 wrapper
負責控制 Node 的資料&該指向哪裡
而這個概念同 Linked List Class Node 跟 Class LinkedList 的關係
建立Class binary_search_tree
同理,一開始二搜樹內是沒有資料的所以將 instructor 初始化為 self.root = None
class binary_search_tree(self):
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
接著我們創建一個 insert() 的function
顧名思義就是讓我們加入資料
插入資料前我們要先檢查樹是否為空 if self.root == None
如果 root == None 代表樹是空的
因此 value 就等於 self.root
如果 root != None 的話
我們就呼叫 private function _insert()
⚠️實際上Python沒有所謂「真正的」private function,所以如果我們看到 _<function_name> 的時候,我們要避免在 Class 外呼叫private_function
接著在這個 _insert() 內要傳入 value 和 root (我們正在查看的current Node)
為什麼要將一個function分成2個的原因是 _insert() 是 「遞迴的」用「一個function 來處理遞迴的事情」 會比 「讓所有邏輯處理都塞在 insert() 」裡來的好
class Binary_search_tree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, value):
#判斷tree是否為空
if self.root == None:
self.root = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, self.root)接著我們開使寫 _insert() 的 function
就像剛剛說的,在 _insert() 裡傳入 value 和 cur_node
而上面 self._insert(value, self.root) 傳入 root的原因是因為所有要新增的Node一定要經過 root
接下來我們就能開始比較「傳入的value 是否 大於 cur_node」了
再來,我們要分成兩個狀況
當 value < cur_node (value小於目前的node)
如果 cur_node.left_child == None 也就是目前的node「沒有」指向 left_child 的 pointer
理所當然 cur_node.left_child = Node(value)
如果 cur_node.left_child != None 也就是目前的node「有」指向 left_child 的 pointer
我們會把 left_child 當成 cur_node 並重新呼叫 _insert()
right_child 同理
最後 else 要處裡 value 與 cur_node 的 value相同的問題前面有提到,二搜樹的value是不能重複的
def _insert(self, value, cur_node):
if value < cur_node.value:
if cur_node.left_child == None:
cur_node.left_child = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value:
if cur_node.right_child == None:
cur_node.right_child = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.right_child)
# value == cur_node.value
else:
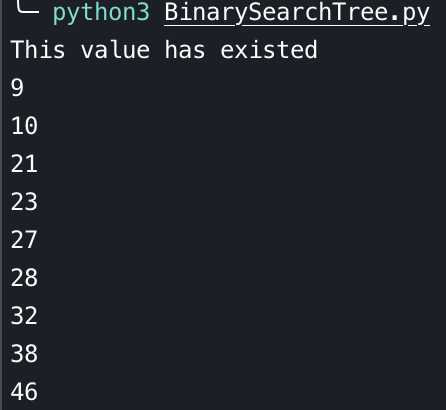
print("This value has existed")
你可能會喜歡:【2020】我的Python學習心路歷程
終於要把樹印出來了(茶
我們先檢查 self.root 是不是 Node
如果 self.root != None (也就是 self.root 有值
我們呼叫 _print_tree(self.root)
同理一樣是用「遞迴」的方式處理,所以將它寫成private function
def print_tree(self):
if self.root != None:
self._print_tree(self.root)同樣印出一棵樹也是從root開始查找
所以cur_node設為self.root
所以 _print_tree(self, cur_node)
def _print_tree(self, cur_node):
if cur_node != None:
self._print_tree(cur_node.left_child)
print(str(cur_node.value))
self._print_tree(cur_node.right_child)最後在class外建立一個 function來幫我們自動建立一個二搜樹
def fill_tree(tree, num_elems=10, max_int=50):
from random import randint
for _ in range(num_elems): #10個 value
cur_elem = randint(0, max_int) #隨機0~50(不含50)的值
tree.insert(cur_elem)
return tree
tree = Binary_search_tree()
tree = fill_tree(tree)
tree.print_tree()執行結果
Python BST 完整程式碼
GitHub: https://github.com/LichtLiu/PG_Data_Structure/blob/main/Binary%20Search%20Tree/BinarySearchTree.py
class Node:
def __init__(self, value=None):
self.value = value
self.left_child = None #smaller
self.right_child = None #greater
class Binary_search_tree:
def __init__(self):
self.root = None
def insert(self, value):
#判斷tree是否為空
if self.root == None:
self.root = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, self.root)
def _insert(self, value, cur_node):
if value < cur_node.value:
if cur_node.left_child == None:
cur_node.left_child = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.left_child)
elif value > cur_node.value:
if cur_node.right_child == None:
cur_node.right_child = Node(value)
else:
self._insert(value, cur_node.right_child)
# value == cur_node.value
else:
print("This value has existed")
def print_tree(self):
if self.root!=None:
self._print_tree(self.root)
def _print_tree(self,cur_node):
if cur_node!=None:
self._print_tree(cur_node.left_child)
print(str(cur_node.value))
self._print_tree(cur_node.right_child)
def fill_tree(tree, num_elems=10, max_int=50):
from random import randint
for _ in range(num_elems): #10個 value
cur_elem = randint(0, max_int) #隨機0~50(不含50)的值
tree.insert(cur_elem)
return tree
tree = Binary_search_tree()
tree = fill_tree(tree)
tree.print_tree()結語
二元樹一直以來是大公司非常注重的觀念之一
想必他在資料結構上有舉足輕重的地位
一定要花時間好好學習
想必在此之後對程式撰寫邏輯上會有莫大的幫助
本篇只有探討到 新增資料 與 印出資料
日後會再補上 刪除與搜尋function
敬請期待
如果對文章內容有任何問題,歡迎在底下留言讓我知道。 如果你喜歡我的文章,可以分享我的文章,讓更多的人看見我的文章。 追蹤我的Instagram,看我分享 #咖啡 #Python 如果這篇文章對你有幫助, 可以幫我在下方按 5 個Like 讓我得到一些回饋, 支持我繼續寫出更多好文章!
- 【SSH】製作SSH key教學
- 【快速架站】什麼是Hexo? 5分鐘快速架站教學
- 【Python】Quick Sort 快速排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】Insertion Sort 插入排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】Selection Sort 選擇排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】Bubble Sort 泡沫排序|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】Binary Search 二分搜尋|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】linear search 線性搜尋|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【Python】什麼是演算法?|演算法介紹、新手快速入門
- 【教學】使用Sourcetree將專案push到Github|GitHub Token 產製與用法






在〈【Python】Binary Search Tree (二元搜尋樹) 資料結構實作(1)〉中有 4 則留言